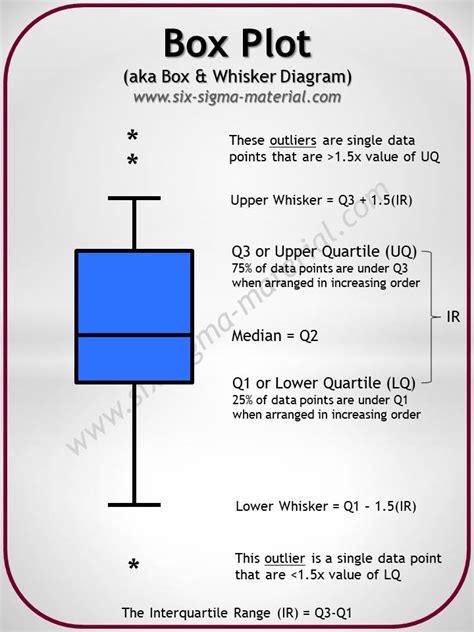
box plot with tight distribution A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, . Arlington’s non-metallic Vapor Boxes for fans, fixtures, and devices are versatile and non-conductive. They feature built-in flanges and gaskets that form a protective barrier against air infiltration. Installation is fast, easy, and secure in new and existing construction for single or .
0 · understanding box plots for dummies
1 · how to make a box and whisker plot
2 · different types of box plots
3 · describing shape of box plots
4 · boxplot shape of distribution
5 · box plot for normal distribution
6 · box plot distribution interpretation
7 · box and whisker chart type
This is a short video to show how the VEBO Outdoor Metal Dog Kennel (PWH202) is assembled
A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.
What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot .
understanding box plots for dummies
how to make a box and whisker plot
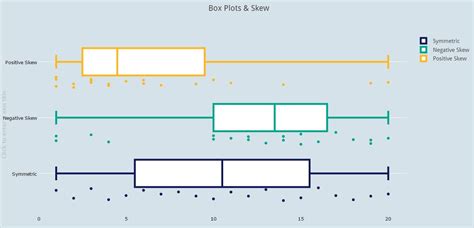
The Box Plot, sometimes also called "box and whiskers plot", combines the minimum and maximum values (i.e. the range) with the quartiles into on useful graph. It consists of a .A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with .A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, . Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median .
Box plots are non-parametric: they display variation in samples of a statistical population without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution [3] (though Tukey's boxplot assumes symmetry for the whiskers .Understanding how to interpret box plots can provide valuable insights into the variability and distribution of a dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the key components of box plots and show you how to interpret .A boxplot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a fantastic tool for visualizing the distribution, spread, and variability of your data. Think of it as a quick summary of your data’s story—it . Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.
A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.The Box Plot, sometimes also called "box and whiskers plot", combines the minimum and maximum values (i.e. the range) with the quartiles into on useful graph. It consists of a horizontal line, drawn according to scale, from the minimum to the maximum data value, and a box drawn from the lower to upper quartile with a vertical line marking the .
A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.” Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median would also indicate a positive skew.
Box plots are non-parametric: they display variation in samples of a statistical population without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution [3] (though Tukey's boxplot assumes symmetry for the whiskers and normality for their length).Understanding how to interpret box plots can provide valuable insights into the variability and distribution of a dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the key components of box plots and show you how to interpret them effectively.A boxplot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a fantastic tool for visualizing the distribution, spread, and variability of your data. Think of it as a quick summary of your data’s story—it shows you where most of your data lies, and even points out those pesky outliers. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.
different types of box plots
A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.The Box Plot, sometimes also called "box and whiskers plot", combines the minimum and maximum values (i.e. the range) with the quartiles into on useful graph. It consists of a horizontal line, drawn according to scale, from the minimum to the maximum data value, and a box drawn from the lower to upper quartile with a vertical line marking the .A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.
A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.” Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median would also indicate a positive skew.
Box plots are non-parametric: they display variation in samples of a statistical population without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution [3] (though Tukey's boxplot assumes symmetry for the whiskers and normality for their length).
Understanding how to interpret box plots can provide valuable insights into the variability and distribution of a dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the key components of box plots and show you how to interpret them effectively.

describing shape of box plots
boxplot shape of distribution
box plot for normal distribution
box plot distribution interpretation
$49.94
box plot with tight distribution|different types of box plots