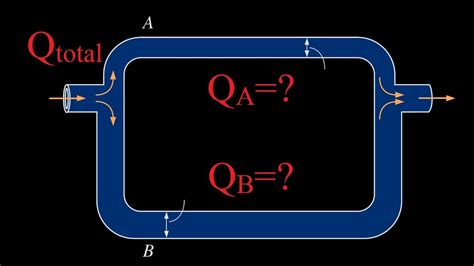
box size distribution affects the flow It seems that pressure losses will have an effect on proportion of distribution. If the two paths have similar designs, ie; the same energy losses, . Get the best deals for Vintage Medical Cabinet at eBay.com. We have a great online selection at the lowest prices with Fast & Free shipping on many items!
0 · how to find flow distribution at junction
1 · how to determine flow distribution
2 · flow distribution at t junction
$25.00
First, we have a duct. Air enters the duct from the left. As the air moves through the duct, it encounters a reducer and then a smaller duct. What do we know about the flow here? Thinking about conservation laws, we can safely assume that every bit of air that enters the . See moreSince we’ve just looked at problems with filtering the airin my last article, you may suspect that this has some relation. And you’re right. A lot of . See moreAir velocity in ducts is a really critical factor in how well ducts do their job of efficiently and quietly moving the right amount of air from one place to . See more
sheet metal fabrication livermore ca
It seems that pressure losses will have an effect on proportion of distribution. If the two paths have similar designs, ie; the same energy losses, .In the static pressure box air supply, the size of the static pressure directly with the flow uniformity related, static pressure distribution more uniform, the velocity distributionThe splitter box and distribution boxes serve as essential devices for dividing a slurry feed into multiple outlet streams, ensuring the uniform distribution of particle sizes and controlled flow to .some researchers (Xu and Niu, 2003) found that the box method is not suitable for flows at low Reynolds numbers, which are usually the cases in displacement ventilation because the jet .
In this study, the effects of two distribution zone designs, i.e., the channel-ridge distribution zone (CRDZ) and dot matrix distribution zone (DMDZ), on the gas distribution uniformity and pressure drop are investigated numerically.
In summary, the conversation discusses the effect of volume and mass airflow on a sealed square box with a round inlet and four smaller outlets. The main question is whether .We find that pore size distributions are a bad predictor of flow distributions in contrast to the distributions of fraction of propagated fluid flow. We begin by presenting numerical simulations . Here we show that for a very wetting liquid close to its melting temperature, strong finite size effects can persist up to large box sizes along the flow direction, typically ∼30 .
Three main modes contribute to the breakup sizes in aerodynamic droplet breakup: the rim node, the remaining rim and the bag breakup modes. However, existing models only consider one . Air velocity in ducts is a really critical factor in how well ducts do their job of efficiently and quietly moving the right amount of air from one place to another. We’ll explore that topic further in a future article but for now, let’s nail down what happens to the velocity as air goes from a larger to a smaller duct. It seems that pressure losses will have an effect on proportion of distribution. If the two paths have similar designs, ie; the same energy losses, the flow will split roughly 50:50. However, if one path has more energy losses than the other, then < .In the static pressure box air supply, the size of the static pressure directly with the flow uniformity related, static pressure distribution more uniform, the velocity distribution
The splitter box and distribution boxes serve as essential devices for dividing a slurry feed into multiple outlet streams, ensuring the uniform distribution of particle sizes and controlled flow to each outlet.
some researchers (Xu and Niu, 2003) found that the box method is not suitable for flows at low Reynolds numbers, which are usually the cases in displacement ventilation because the jet flow decays rapidly. In addition, the criteria to determine the box size seems contradictory, In this study, the effects of two distribution zone designs, i.e., the channel-ridge distribution zone (CRDZ) and dot matrix distribution zone (DMDZ), on the gas distribution uniformity and pressure drop are investigated numerically. In summary, the conversation discusses the effect of volume and mass airflow on a sealed square box with a round inlet and four smaller outlets. The main question is whether the velocity and mass airflow would be different for each outlet due to the varying length from the inlet.
We find that pore size distributions are a bad predictor of flow distributions in contrast to the distributions of fraction of propagated fluid flow. We begin by presenting numerical simulations of fluid flow in a two-dimensional porous medium.
Here we show that for a very wetting liquid close to its melting temperature, strong finite size effects can persist up to large box sizes along the flow direction, typically ∼30 particle diameters.Three main modes contribute to the breakup sizes in aerodynamic droplet breakup: the rim node, the remaining rim and the bag breakup modes. However, existing models only consider one mode and are, therefore, unable to predict the size distribution.
Air velocity in ducts is a really critical factor in how well ducts do their job of efficiently and quietly moving the right amount of air from one place to another. We’ll explore that topic further in a future article but for now, let’s nail down what happens to the velocity as air goes from a larger to a smaller duct. It seems that pressure losses will have an effect on proportion of distribution. If the two paths have similar designs, ie; the same energy losses, the flow will split roughly 50:50. However, if one path has more energy losses than the other, then < .In the static pressure box air supply, the size of the static pressure directly with the flow uniformity related, static pressure distribution more uniform, the velocity distributionThe splitter box and distribution boxes serve as essential devices for dividing a slurry feed into multiple outlet streams, ensuring the uniform distribution of particle sizes and controlled flow to each outlet.
some researchers (Xu and Niu, 2003) found that the box method is not suitable for flows at low Reynolds numbers, which are usually the cases in displacement ventilation because the jet flow decays rapidly. In addition, the criteria to determine the box size seems contradictory, In this study, the effects of two distribution zone designs, i.e., the channel-ridge distribution zone (CRDZ) and dot matrix distribution zone (DMDZ), on the gas distribution uniformity and pressure drop are investigated numerically. In summary, the conversation discusses the effect of volume and mass airflow on a sealed square box with a round inlet and four smaller outlets. The main question is whether the velocity and mass airflow would be different for each outlet due to the varying length from the inlet.We find that pore size distributions are a bad predictor of flow distributions in contrast to the distributions of fraction of propagated fluid flow. We begin by presenting numerical simulations of fluid flow in a two-dimensional porous medium.
sheet metal fabrication jobs in birmingham
Here we show that for a very wetting liquid close to its melting temperature, strong finite size effects can persist up to large box sizes along the flow direction, typically ∼30 particle diameters.
how to find flow distribution at junction
sheet metal fabrication jobs melbourne
how to determine flow distribution
flow distribution at t junction
Explore a wide range of our Vintage Metal File Box selection. Find top brands, exclusive offers, and unbeatable prices on eBay. Shop now for fast shipping and easy returns!
box size distribution affects the flow|flow distribution at t junction